
Based on the median policy rate prediction provided at the June FOMC meeting, it is anticipated a slowdown in the U.S. economy in 2022–2023. Real earnings will be safeguarded and growth will be sustained over the medium term with the support of price stability and reduced inflation.
The US economy accelerated into 2021, but the combination of growth and global supply chain bottlenecks drove inflation higher than planned. Interest rate increases were set for March 2022, which are expected to chill the economy.
What Kind of Economy Does the United States Have?
The American economy is a mixed one. Although it often intervenes in the market, such as through the Federal Reserve’s quantitative easing initiatives, the United States administration promotes free market activities.
What Is the Size of the American Economy?
Money may refer to the amount of dollars in circulation or the amount of credit in the economy, although GDP is easier to calculate in precise numbers. With the exception of a brief decline in 2020 during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. GDP has recently stayed over $20 trillion.
The State of the American Economy In 2022
With fourth-quarter GDP growth of 6.9 percent, the economy finished 2021 strong. Growth was accompanied by a sharp increase in inflation, which reached 7% year over year, much beyond the Federal Reserve’s objective of 2%.
At the end of 2021, the unemployment rate was only 3.9 percent, down from 6.4 percent at the beginning of the year. When the economy collapsed in April 2020, unemployment reached a pandemic high of 14.7%.
The Federal Reserve kept the fed funds rate at or close to zero, which supported economic development. In addition, the Federal Reserve made record purchases of mortgage and Treasury securities during this time. However, the Board indicated at its meeting in December 2021 that it would hasten the tapering of its purchases of Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities. This move was a sign that higher interest rates were approaching.
Unemployment
The Federal Reserve predicted a 2022 unemployment rate of 3.5 percent based on the same data in March 2022. It was predicted that the rate will remain at that level in 2023 and increase to 3.6 percent in 2024.
The rate reached its highest point in April 2020 at almost 15% as a result of layoffs brought on by the epidemic. As you can see, many have lost their jobs. People are in a difficult financial situation. If you urgently need money, you can always take a 100 dollar loan to pay for the services you need.
Economic Expansion
The Federal Open Market Committee meeting on December 15 revealed the December 2021 estimate, which predicted that the US GDP will rise by 4% in 2022. It was predicted that after that, the growth rate would fall to 2.2 percent in 2023.
Then further decline to 2 percent in 2024. The Fed revised its earlier predictions during its meeting on March 16, 2022, forecasting lower GDP growth of 2.8 percent in 2022, followed by a growth of 2.2 percent in 2023.
Jobs
Every year, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases an occupational outlook that includes extensive information on each sector and profession. The BLS anticipates around 12 million job growth in total employment between 2020 and 2030.
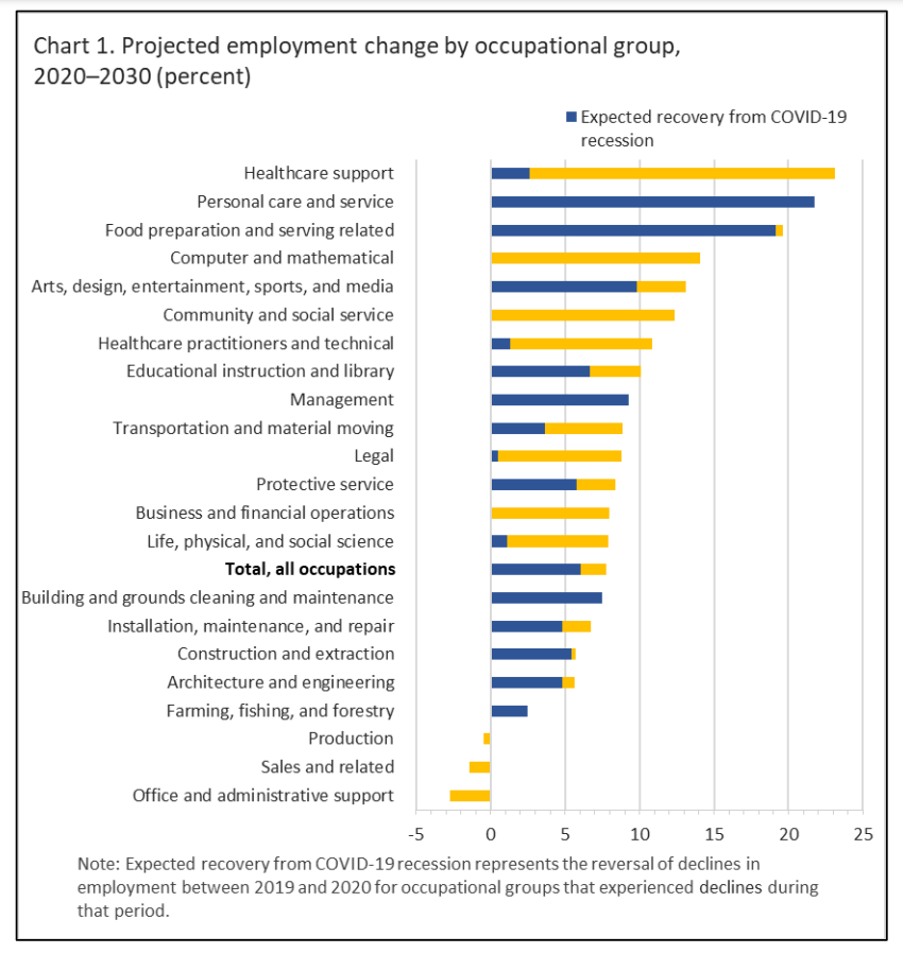
Over the next ten years, 3.3 million jobs in the healthcare and social support sectors are expected to be added, bringing the total to 23.1 million by 2030. While e-commerce is still expanding, the majority of the industrial and retail sectors will continue to see employment losses. The consumer rental and wired communications sectors will also see decreases.
Inflation
According to forecasts, the core inflation rate would be 4.1 percent in 2022, and 2.6 percent in 2023. The Federal Reserve prefers to base monetary policy on the core inflation rate, which excludes volatile food and gas costs.
Rates of Interest
The FOMC held an emergency meeting in March 2020 to discuss the COVID-19 pandemic’s economic effects, and as a result, the fed funds rate was reduced to a range of 0% and 0.25%. The FOMC declared that it would raise interest rates for the first time since 2018 at its meeting on March 16, 2022, in an effort to combat rising inflation. The target range was widened to 0 to 0.25 to 0.25 to 0.50 percent, an increase of 0.25 percent.
Predicted a gradual increase in the target fed funds rate to 1.9 percent in 2022 in its March 2022 projections. In 2023 and 2024, the target rate is expected to increase to 2.8 percent.
The Fed has been working to maintain low long-term rates to reduce the cost of borrowing money and thereby promote both consumer and business spending.
It started up its quantitative easing (QE) program again and soon increased the size of QE purchases to infinity. The Federal Reserve said in March 2020 that it will buy $200 billion in mortgage-backed securities as well as $500 billion in U.S. Treasury bonds.
The Fed raises prices and decreases the return (or yield) on these long-term notes by purchasing bank assets, so reducing supply in the Treasury market. These rates serve as the industry standard for corporate bonds and long-term fixed-rate mortgages.
The dollar’s demand has an impact on Treasury rates as well. High demand forces yield to decline. Investor demand for this ultra-safe investment may decline if the world economy improves, raising yields and interest rates.
Price of Gas And Oil
According to the EIA’s energy projection through 2050, oil prices will increase. The information indicates that, in a constant 2021 currency, the average Brent oil price might rise to a peak of $170 per barrel in 2050. Administration initiatives to enhance the generation of renewable energy in an attempt to halt global warming are not included in this projection.
Changing Climate
The Federal Reserve is worried about how the economy may be impacted by climate change. According to research from the Richmond Fed, if the nation keeps up its high emission rate, climate change may cause the yearly GDP growth rate to fall by up to a third of the historical norm.
As in previous years, hurricanes and wildfires caused damage in the United States in 2020. Hurricanes, floods, and wildfires were among the climate change-related natural catastrophes that caused $210 billion in damage globally in 2020.
Losses compensated by insurance in the United States reached $82 billion in 2020 and about $57 billion in 2019. As a result of global warming, damage claims have been greater and more common.
To Sum Up
Inflation and rates of interest are expected to rise in the next few years, while the price of gas and oil is predicted to increase as well. The Fed is concerned about the potential impact of climate change on the economy, particularly in light of recent natural disasters. Despite these challenges, the economy is projected to continue growing.


